Red, itchy, and painful skin is often the sign of a troubling skin condition. It is often difficult to pinpoint the cause of many skin issues, so some expert advice may help you decide if you need to seek medical help.
The good news is that most skin conditions can be managed and generally are not life-threatening. Listed below is some helpful information and advice for 15 of the most troubling skin conditions.

Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects nearly 14 million Americans. Rosacea is more likely to develop in pale-skinned women. The condition occurs when facial blood vessels redden and blush or flush easily.
There are four subtypes of this skin condition:
- Ocular rosacea: swollen, red eyelids and eye irritation, sensation of something in eye
- Papulopustular rosacea: irregular appearance, acne-like breakouts, swelling
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (most common form): flushing, visible blood vessels, redness
- Phymatous rosacea: bumpy texture, thickening of the skin
There seems to be a genetic connection to rosacea, but there are also some factors that can trigger flare-ups like sun exposure, hot weather, cigarette smoking, alcohol, and spicy foods.
Currently, there is no definitive test to diagnose rosacea.
Treatment typically comes in the form of topical medications and oral antibiotics.
Rosacea Symptoms
- Red, acne-like breakouts
- Thick, bumpy skin
- A blush that doesn’t go away
- Eye irritation and vision problems
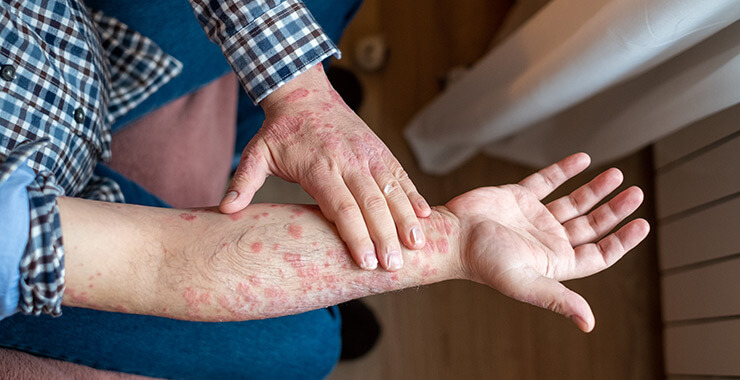
Eczema
Eczema is a broad term for multiple conditions that cause irritated, inflamed, and itchy skin. The most common type of eczema is known as atopic dermatitis. This troubling skin condition affects 10 to 20 percent of children worldwide, often appearing before age 5.
Skin examinations and medical history are used to diagnose eczema. Treatment goals include reducing discomfort and preventing flare-ups by identifying skin condition triggers.
Studies are showing that there may be a shared genetic connection between asthma, hay fever, and eczema.
Atopic Eczema Symptoms
- Raised red, scaly patches
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Dry, itchy skin
- Mostly found on hands, back of knees, and inside elbows
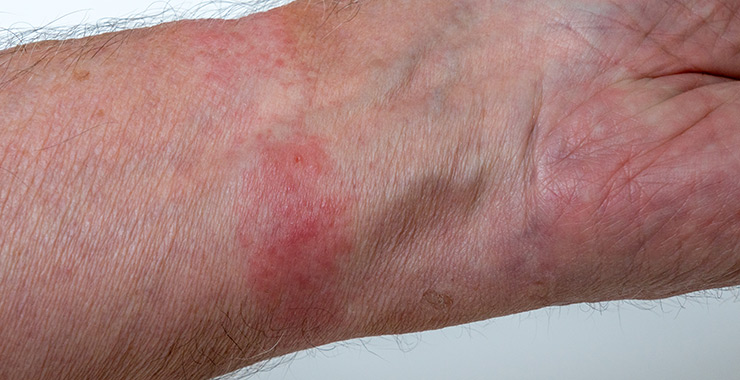
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is another form of eczema that results in irritated skin after it encounters something that triggers a reaction. There are two types of contact dermatitis:
- Allergic contact dermatitis which is a skin irritant that presents several days after exposure to an allergen, like latex or poison ivy
- Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when skin touches an irritant like detergents, nickel jewelry, or makeup
Common treatments include avoidance of allergens and irritants, topical medication, anti-itch medication like Benadryl, and steroid ointments.
Urgent care facilities play an important role in helping to identify and treat contact dermatitis and other allergic reactions quickly.
Contact Dermatitis Symptoms
- Burning, itchy skin
- Blistering
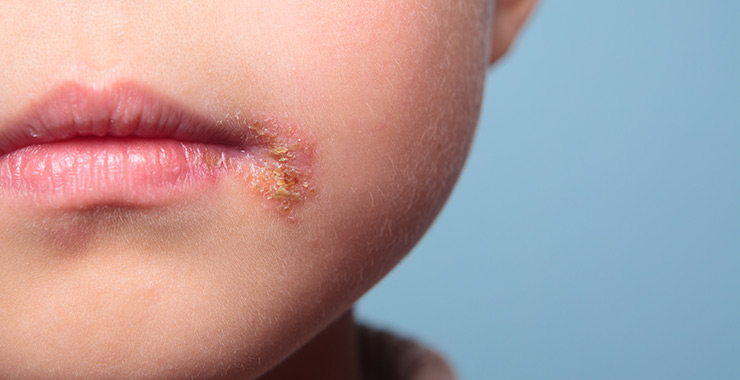
Impetigo
Impetigo is caused by group A streptococcus. It is most common in children. This highly contagious skin condition most often appears around the mouth and nose, and sometimes on the arms and legs.
The condition is most often treated with antibiotic creams and oral antibiotics.

Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis, also known as scalp eczema, is similar to dandruff. Treatment recommendations include washing the scalp with dandruff shampoo with ingredients like salicylic acid, selenium, zinc pyrithione, or coal tar.
Your medical provider may also prescribe an antifungal shampoo.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Symptoms
- Crusty, scaly patches on the scalp
- Can also be found on the face and chest
- Skin looks flaky and greasy
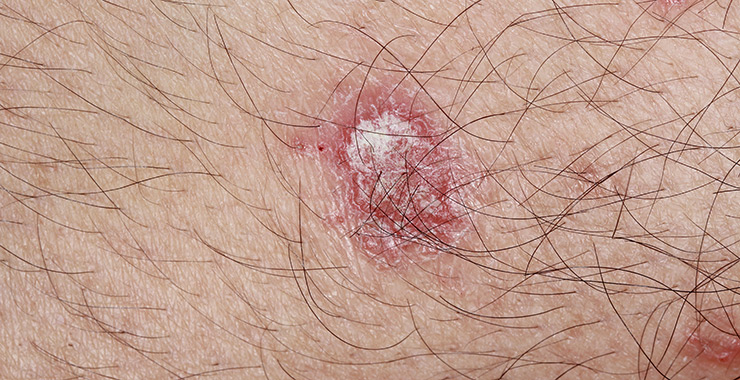
Actinic Keratosis
Actinic lesions are a precancerous skin condition related to sun exposure. People who are 50 or older with fair skin who have spent a lot of time in the sun (without sun screen) are more likely to get actinic keratosis than those who do not have these factors.
Treatment includes a topical prescription product or cryotherapy.
Actinic Keratosis Symptoms
- Flat, scaly skin patches
- Rough, flaky skin
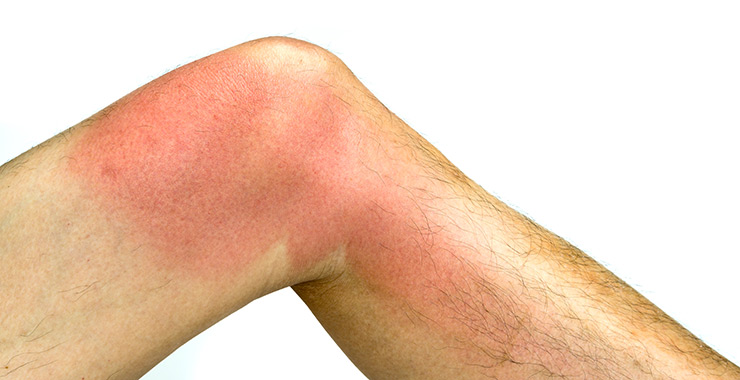
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that enters the body through cracks or tiny breaks in the skin. It can appear anywhere on the body and is often associated with athlete’s foot.
The CDC reports that people who are overweight, and those with diabetes, or a compromised immune system are at a higher risk for contracting cellulitis.
Oral antibiotics are the most common treatment for this skin condition. Although, in serious cases, an IV antibiotic treatment may be needed.
Cellulitis Symptoms
- Red, warm, tender skin
- Swelling and pain
- Blisters may appear
- Has an orange peel-like texture
- May present with fever and chills
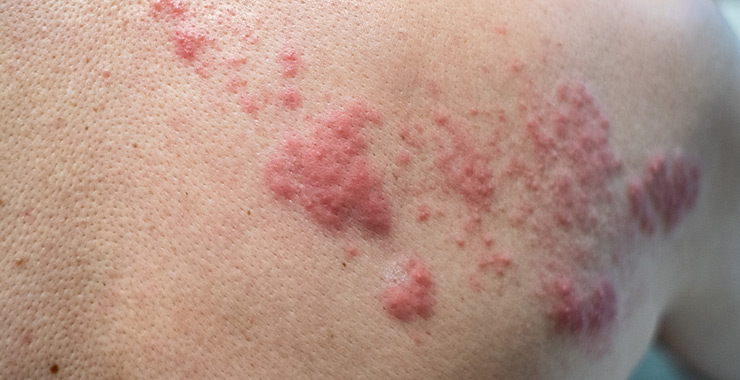
Shingles
Shingles come from the varicella-zoster virus, also known as chickenpox. If a person contracted chickenpox as a child, after recovery the virus stayed in the body and moved to the nerves. Later in life, the virus can reactivate and cause shingles.
A recombinant zoster vaccine is recommended for adults 50 years and older and for adult 19 years and older who have a weakened immune system due to disease or other medical treatments. Consult with your medical provider before getting a recombinant vaccine.
Shingles Symptoms
- Painful skin rash, with blisters
- Fever
- Headache
- Chills
- Upset stomach
- Long-term nerve pain
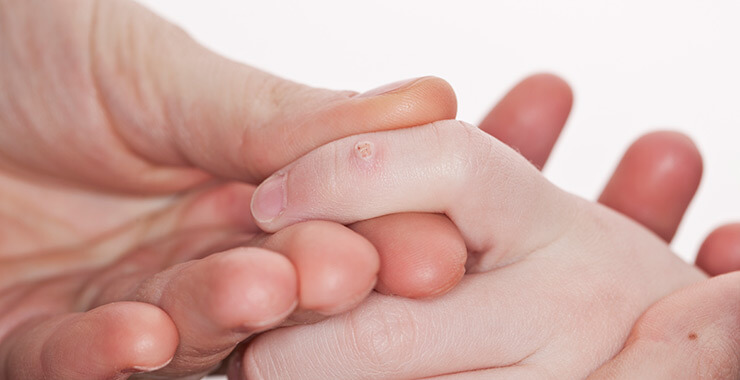
Warts
Warts are small, hard, painless growths on the skin that are rough to the touch. HPV, or the human papillomavirus, causes the top layer of the skin to overproduce keratin, which then become warts. Warts are contagious through skin-to-skin contact.
Warts can appear on any part of the body but are mostly found on the hands and feet. Without treatment, about 65% of wart infections go away on their own, but a medical provider will likely recommend removing them.
Common warts can be treated with a topical, 17 percent salicylic acid solution, used daily for a few weeks. Before applying the product, soak the wart in warm water for a few minutes.
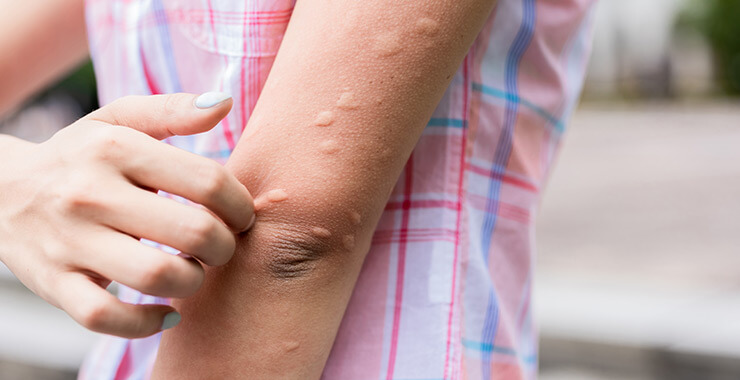
Hives
Hives are itchy, raised welts that typically form in clusters. Stress, illness, friction, extreme cold or sun exposure, or an allergic reaction can cause hives.
With this type of allergic reaction, the body releases histamine, and other chemicals into the blood. This causes itching, swelling, and burning sensation. People with other allergies, such as hay fever, often get hives.
Treatment of hives typically involves antihistamines or corticosteroids.
Hives Symptoms
- Clusters of raised welts
- Itchy, warm skin
- Pinkish or red in color
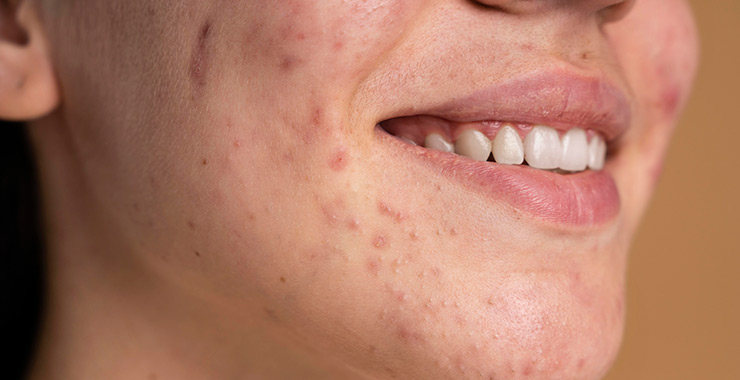
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles under the skin become clogged with sebum. Sebum is a naturally occurring oil that helps keep skin from drying out, but occasionally dead skin cells mixed with sebum plug the pores, which leads to outbreaks of lesions, commonly called pimples or zits.
Doctors refer to enlarged or plugged hair follicles as comedones.
Any person can get acne, although it is most common in and young adults.
Treatment of acne can come in the form of prescription medications, hormone therapy, topical creams, and light therapy.
Acne Symptoms
- Pustules of pimples with pus at the top
- Papules of infected hair follicles
- Nodules of painful, red lumps below the skin surface
- Cysts of larger, painful, pus-filled bumps
The following do not cause acne but could make the condition worse.
- Some studies show that eating high glycemic foods like French fries, white bread, white rice, pastries, and potato chips may make acne worse
- Emotional and/or physical stress
- Friction from sports helmets, tight clothes, or backpacks
- Environmental irritants, like pollution and high humidity
- Touching the skin too often and squeezing or picking at blemishes
- Washing and scrubbing the skin too hard and too often
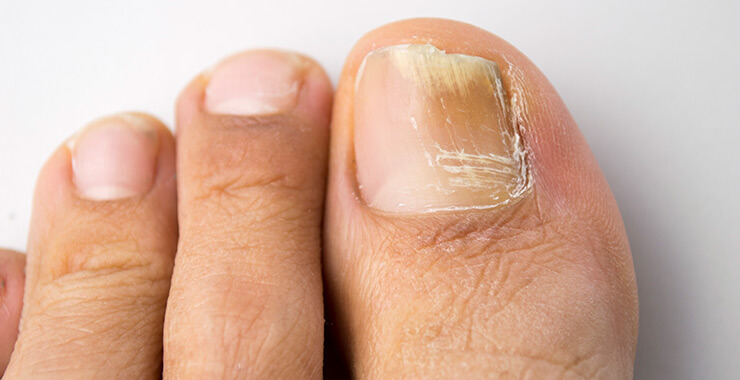
Fungal Nail Infection
This skin condition is an overgrowth of fungus near or under the toenails or fingernails. A fungal infection causes the nail edges to begin flaking or crumbling away and the nail surface may have a whitish-yellow scaling.
Treatment depends on which type of fungi caused the infection, but most doctors will prescribe an oral or topical medication. In severe cases, the affected nail may need to be removed.
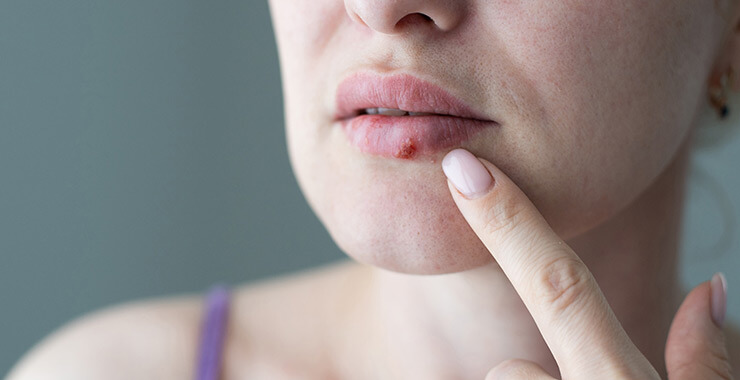
Cold Sore
The herpes simplex virus causes cold sores. These red, fluid-filled blisters are typically found around the mouth may last up to two weeks, then return periodically.
Antiviral creams may speed up healing and cold packs can help reduce pain. There are also some studies indicating that pure aloe vera gel can promote healing.
Cold Sore Symptoms
- Burning, tingling sensation around mouth
- Itchiness and pain
- Red, scaly blisters
Moles
Common moles are growths that form when skin cells bunch together with surrounding tissue.
Almost every adult has a few moles. Adults who have light skin often have more moles. Most people have 10 to 40 moles on their skin. This is considered normal.
However, it is important to check moles regularly for any changes in their appearance, such as an increase in size or change in color. If you notice any changes, let their doctor know as soon as possible.
A Note on Skin Conditions
Many skin conditions are harmless, while others can cause discomfort, ongoing problems, and permanent scarring.
Please remember that no one needs to deal with skin issues alone. Find a doctor to help ensure that you receive the correct diagnosis and best possible treatment plan.